- Direct reduction in power bill
- Reduction in maintenance cost due to reduction in failures of the fixtures
- Incidental reduction in power bill due to more units shifting to a lower rate slab
- Reduction in heat generation thereby reducing requirement for cooling leading to a saving in air conditioning consumption
- LEDs emit almost NIL UV or Infrared ray
- LEDs are more energy efficient, evolving and non-hazardous
- The life of LEDs can be at least 10 times higher than the conventional lighting without any loss in the lighting output over a much longer period of time, say minimum 36,000 hours (i.e. 1,500 days or about 49 months for a continued use of 24 hours per day)
- Long service life.
- Step less dimming in combination with electronic ballast.
- Smallest dimensions.
- High switching capability.
- Instant light when switched on.
- Broad operating temperature.
- High color saturation without filtering.
- Mercury-free.
LED Stands for Light Emitting Diode. It is a semiconductor device that emits light when a current is passed through it. LED technology is constantly evolving and found in a wide range of products in our everyday life. Typical applications over the years have been household appliances, telecommunications, signal technologies and indicator devices; more recently white LED’s have allowed the technology to become a very efficient modern light source.

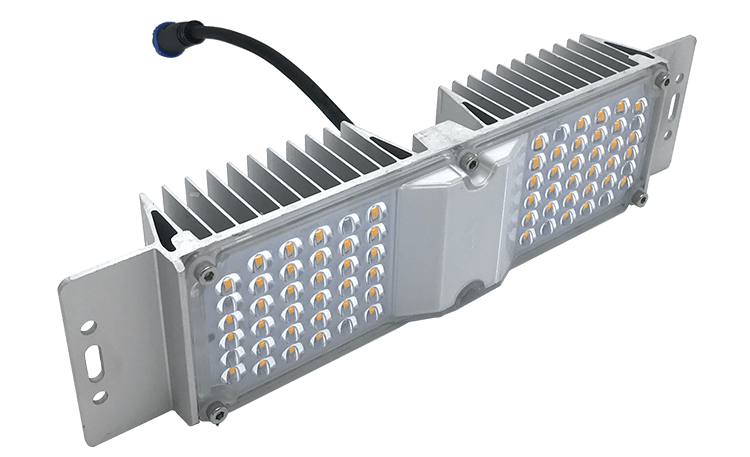
LED Light Engines are available in a number of different packages; we use the following in our LED luminaries
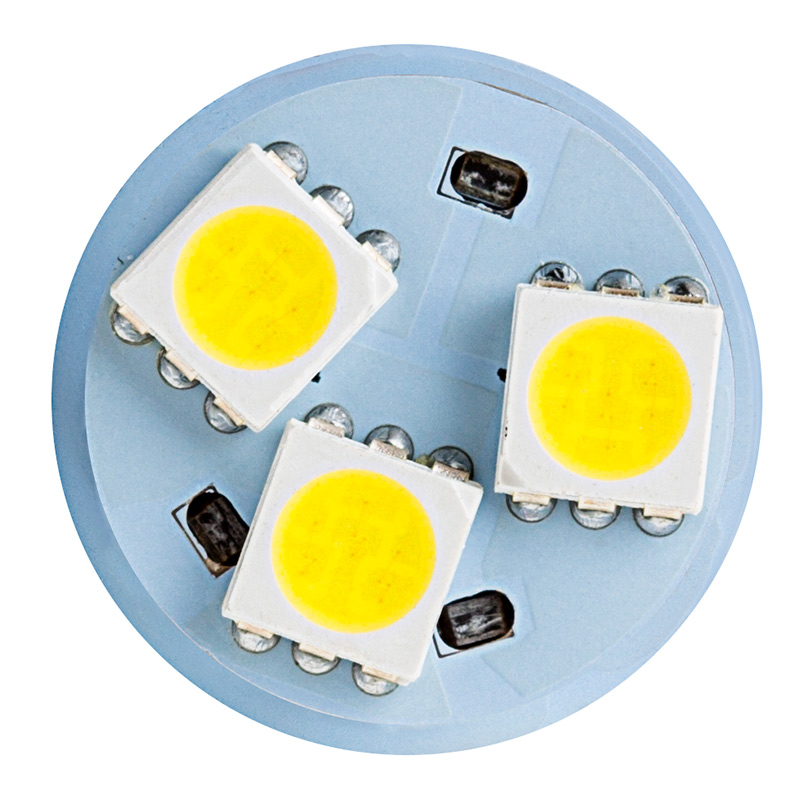
SMD Stands for Surface Mounted Device, it is a very small LED package that is soldered and mounted directly to a PCB (Printed Circuit Board). This makes the technology ideal for edge lighting LED panels and for the LED Tubes. We utilise a large number of small LED’s to ensure uniformity of light, with no light hot (bright) spots.


COB Stands for Chip On Board, these compact high flux density light sources deliver uniform high quality illumination without pixilation or the multiple shadow effect caused by LED component based solutions, enabling both diffused and directional lamp replacements for a wide range of applications
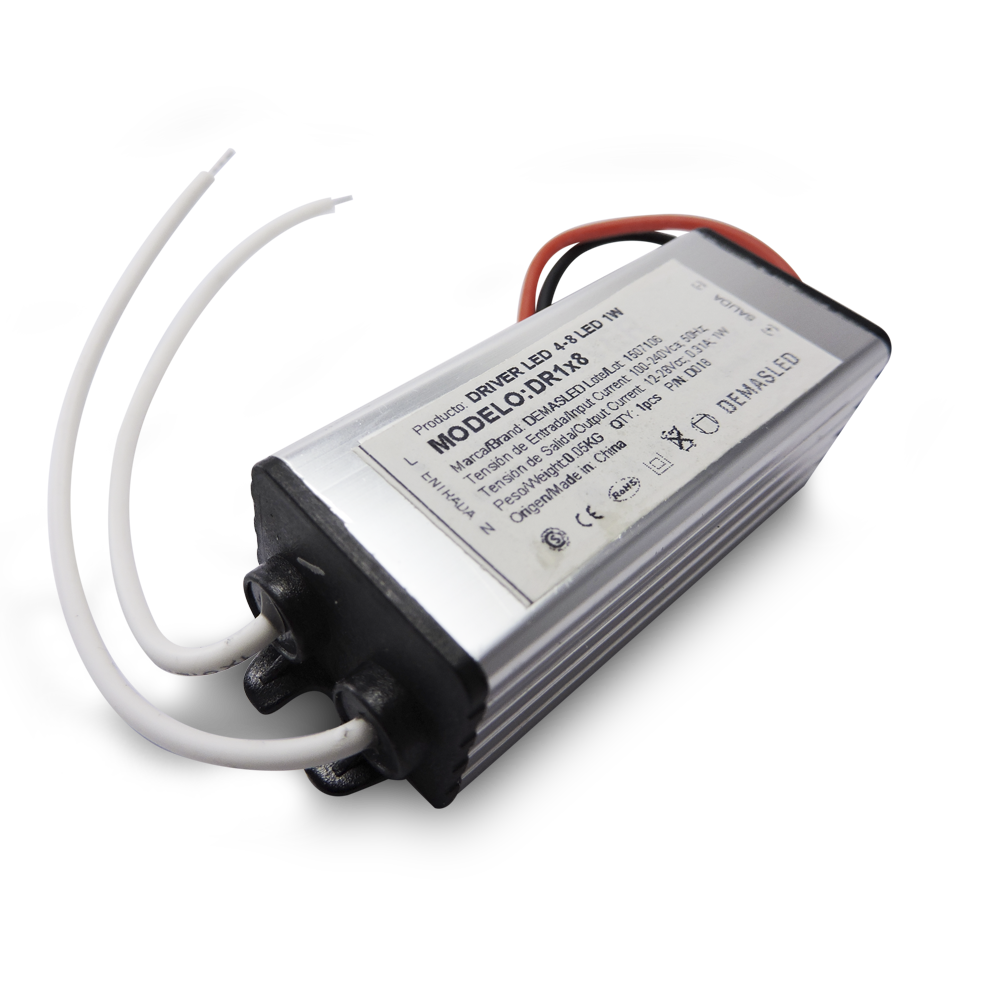
An LED driver is an electrical device which regulates the power to an LED or a string (or strings) of LEDs. An LED driver responds to the changing needs of the LED, or LED circuit, by providing a constant quantity of power to the LED as its electrical properties change with temperature. An LED driver is a self-contained power supply which has outputs that are matched to the electrical characteristics of the LED or LEDs. LED drivers may offer dimming by means of pulse width modulation circuits and may have more than one channel for separate control of different LEDs or LED arrays. The power level of the LED is maintained constant by the LED driver as the electrical properties change throughout the temperature increases and decreases seen by the LED or LEDs. Without the proper driver, the LED may become too hot and unstable, therefore causing poor performance or failure.